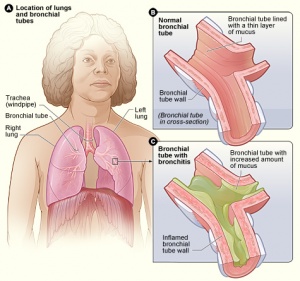
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to your lungs. It causes a cough that often brings up mucus. It can also cause shortness of breath, wheezing, a low fever, and chest tightness. There are two main types of bronchitis: and chronic. Chronic bronchitis is one type of (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). The inflamed bronchial tubes produce a lot of mucus. This leads to coughing and difficulty breathing.
Cigarette is the most common cause. Breathing in air pollution, fumes, or dust over a long period of time may also cause it. To diagnose chronic bronchitis, your doctor will look at your signs and symptoms and listen to your breathing.
You may also have other tests. Chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition that keeps coming back or never goes away completely. If you smoke, it is important to quit. Treatment can help with your symptoms. It often includes medicines to open your airways and help clear away mucus.
You may also need. May help you manage better in daily life.
NIH: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
KEYWORDS for searching the Internet and other reference sources Asthma Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Influenza Lung disease Pneumonia What Is Bronchitis? When a person has bronchitis, the tissue lining the airways swells, narrowing the air passages and making it difficult to breathe.
The inflamed airways produce larger amounts of a thick, slippery substance called mucus (MYOO-kus), which can clog the air passages and complicate breathing even more. The excess mucus usually is coughed up.
In addition, in bronchitis, the cilia (fine, hairlike structures on the surface of the cells lining the airways that help cleanse the airways of inhaled particles) become less able to clear impurities and bacteria from the airways, making it harder for the person to fight off lung infection. The disease can be brought on by a viral or bacterial infection, but it also can be the result of smoking or living or working in areas where there is heavy air pollution and dust. trachea (TRAY-kee-uh) is the windpipe—the firm, tubular structure that carries air from the throat to the lungs.
Types of bronchitis There are three kinds of bronchitis. Acute bronchitis comes on quickly and is typically the result of a bad cold or flu. It generally lasts about 10 days. In severe cases, a bad cough can persist up to a month as the bronchi heal. The acute form also can be caused by an allergy or by inhaling irritating substances in the air, such as smoke from a fire. Chronic (KRAH-nik, persistent or recurring) bronchitis is caused by continuing or repeated inflammation of the lungs over a period of time, at least 2 to 3 months, and it can persist or come and go over years.
Bronchitis Case Study Presentation
Excess mucus is produced, and the lining of the bronchi thickens. This leads to a bad cough and restricted airflow. People who smoke heavily and those with chronic lung disease are most likely to experience chronic bronchitis. The third type, asthmatic bronchitis, is seen in people with persistent asthma. Who Gets Bronchitis and How? No matter who they are, what their job, or where they live, people who smoke cigarettes are more likely to experience chronic bronchitis.
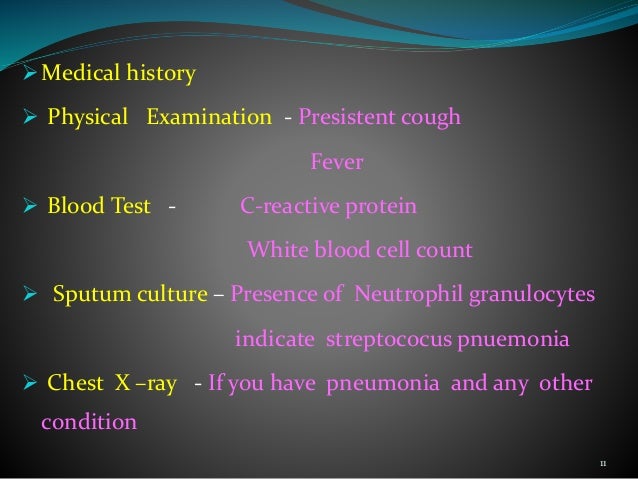

The American Lung Association reports that the disease develops in nearly nine million people in the United States every year. Bronchitis affects people of all ages, but those who are 45 years or older get it more often, and women are more susceptible than men. More than 10 million people have bouts of acute bronchitis every year; most are children less than 5 years of age, who typically get it in winter and early spring. The viruses that can cause acute bronchitis are contagious. People can get a viral infection from someone who is infected if they come into contact with that person's respiratory fluids. The virus also can spread from person to person through the air by way of the droplets from a sneeze or cough. Generally, chronic bronchitis is not contagious.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Bronchitis? Bronchitis symptoms often mimic those of a cold. A cough that brings up mucus is common. Symptoms of acute bronchitis may include wheezing, tiredness, chest pain, and difficulty breathing.
If the cause is a viral or bacterial infection, the patient may have a fever. Chronic bronchitis usually is marked by a cough that lasts 3 months or longer, tightness in the chest, and trouble breathing.
Bronchitis often is confused or lumped together with other conditions. The doctor usually will rule out other causes for coughing and breathing problems to make the diagnosis. Besides listening to a person's breathing, the doctor may order a chest X ray to check for pneumonia or a lung function test to check for asthma. How Is Bronchitis Treated?
Bronchitis Case Scenario
Many doctors prescribe antibiotics for acute bronchitis, although these medicines often do not work because they cannot cure viral infections. Bronchodilator.
drugs may be prescribed to help open the airways, either in pill form or as a spray inhaler. Over-the-counter medications can be used to minimize pain and lessen cough. Patients also are advised to get a lot of rest, eat a well-balanced diet, and drink lots of fluids.
It is suggested that people who have chronic bronchitis stop smoking and avoid dust, fumes, and cold or dry air. Cough medicine and vaporizers may help. Antibiotics often are prescribed when symptoms flare up acutely in a person with chronic bronchitis. Kicking Butts When a smoker quits smoking, it takes only 20 minutes to feel better.